Jian Hu, Xiangjie Li, Kyle Coleman, Amelia Schroeder, Nan Ma, David J Irwin, Edward B Lee, Russell T Shinohara, Mingyao Li
Published in Nature Methods
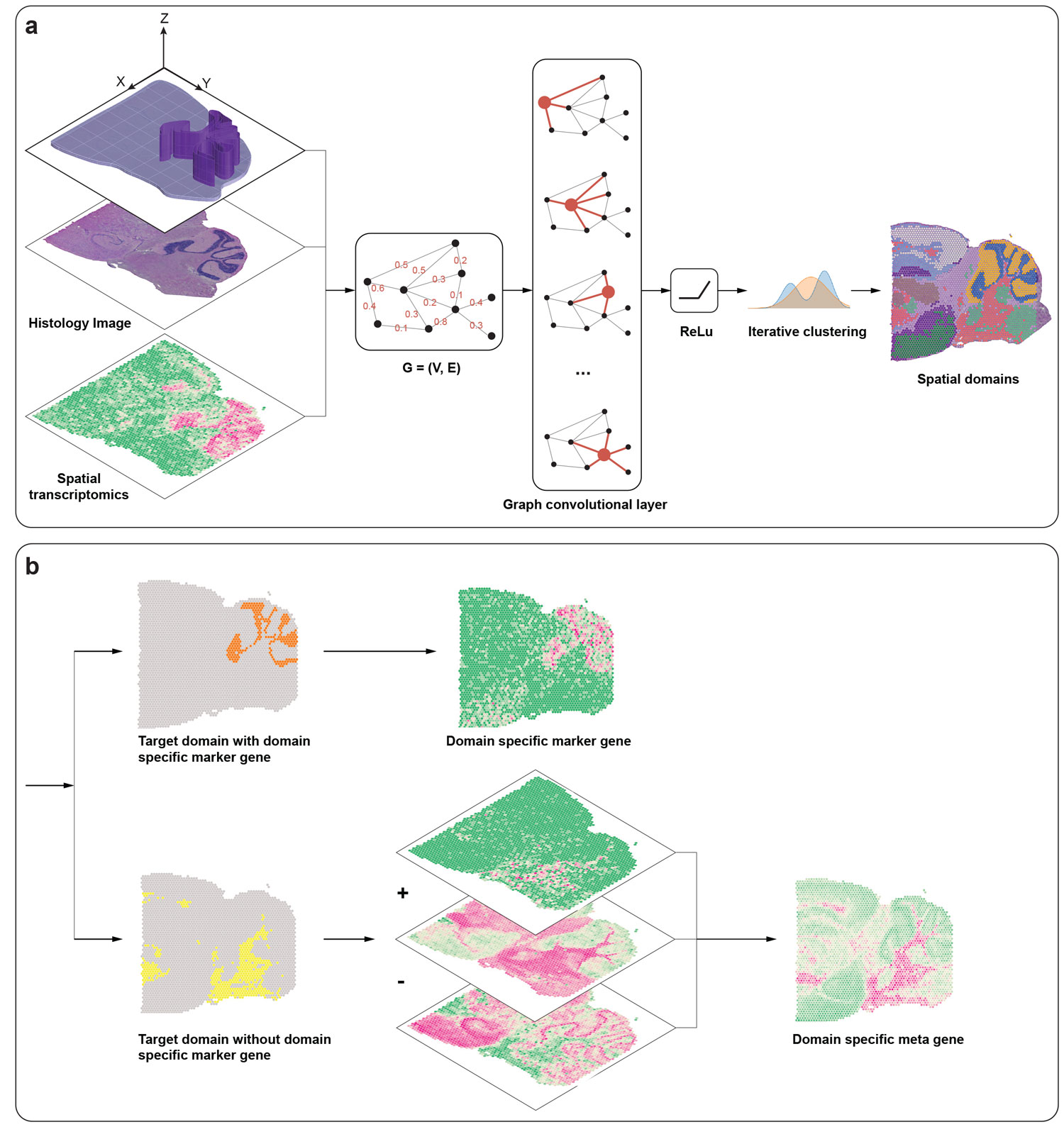
Recent advances in spatially resolved transcriptomics (SRT) technologies have enabled comprehensive characterization of gene expression patterns in the context of tissue microenvironment. To elucidate spatial gene expression variation, we present SpaGCN, a graph convolutional network approach that integrates gene expression, spatial location and histology in SRT data analysis. Through graph convolution, SpaGCN aggregates gene expression of each spot from its neighboring spots, which enables the identification of spatial domains with coherent expression and histology. The subsequent domain guided differential expression (DE) analysis then detects genes with enriched expression patterns in the identified domains. Analyzing seven SRT datasets using SpaGCN, we show it can detect genes with much more enriched spatial expression pat- terns than competing methods. Furthermore, genes detected by SpaGCN are transferable and can be utilized to study spatial variation of gene expression in other datasets. SpaGCN is computationally fast, platform independent, making it a desirable tool for diverse SRT studies.
